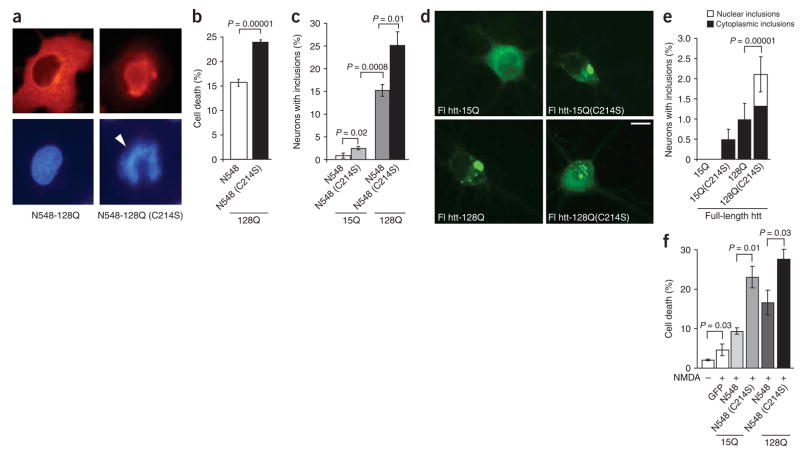
Figure 4.
Enhanced toxicity of palmitoylation-resistant mutant htt. (a,b) COS cells transfected with N548-128 and N548-128(C214S) were scored for toxicity by analyzing nuclei for changes associated with cell death. Cell death was significantly (P = 10−5) induced by the expression of N548-128(C214S). Representative images show a normal nucleus and an apoptotic nucleus (arrowhead). (c–e) Rat cortical neurons were transfected with truncated htt (N548) or full-length htt (flhtt) constructs as indicated, and stained with htt antibody. (c) The percentage of neurons containing inclusions increased in neurons expressing N548-15(C214S) (2.5 ± 0.35%), increased still further in neurons expressing N548-128 (15.17 ± 1.3%) and was maximal in neurons expressing N548-128(C214S) (25.08 ± 3.1%). (d) Representative images showing neurons expressing the indicated flhtt constructs. Scale bar, 5 μm. (e) The percentage of neurons containing inclusions increased in neurons expressing flhtt-15Q(C214S) (0.5 ± 0.27%), increased still further in neurons expressing flhtt-128Q (1 ± 0.41%) and was maximal in neurons expressing flhtt-128Q(C214S) (2.1 ± 0.44%). There was a significant (P = 10−5) increase in the percentage of cells with nuclear inclusions in neurons expressing flhtt-128Q(C214S). (f) Rat cortical neurons transfected with the indicated htt constructs were treated with NMDA for 10 min and processed for the TUNEL assay. The percentage of cell death was significantly greater in transfected cells expressing N548-15Q (C214S) (23.16 ± 5.2; P = 0.01) and N548-128Q(C214S) (27.75% ± 4.7; P = 0.03), demonstrating that the loss of palmitoylation significantly reduces cellular viability.