Figure 5.
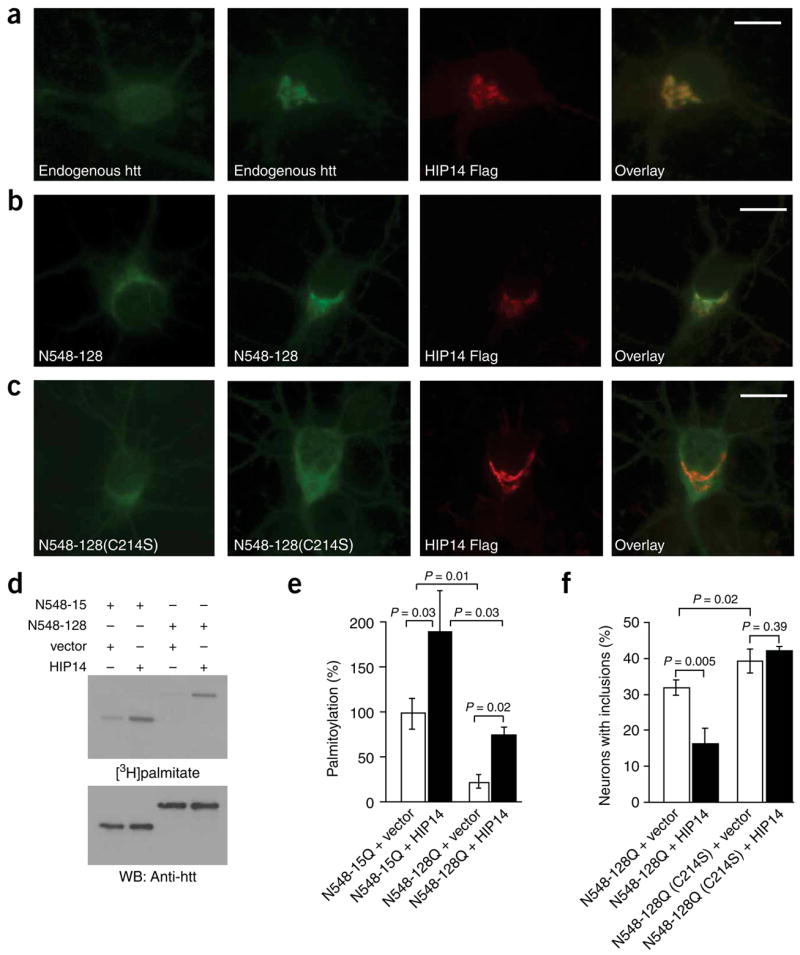
HIP14 influences the distribution and catalyzes the palmitoylation of htt in neurons. (a) Cortical neurons transfected with control vector (left) or with FLAG-tagged HIP14 were labeled with the appropriate antibodies. The overexpression of HIP14 resulted in marked redistribution of endogenous htt to the Golgi. Scale bar, 5 μm. (b,c) Cortical neurons transfected with N548-128Q-GFP or N548-128Q(C214S)-GFP alone (left) or with HIP14-FLAG were labeled with the appropriate antibodies. Scale bar, 5 μm. (b) Partial redistribution of N548-128Q-GFP was observed in the presence of HIP14. (c) No effect in the distribution of palmitoylation-resistant htt (N548-128Q(C214S)-GFP) was observed in the presence of HIP14. (d) COS cells transfected with N548-15Q or N548-128Q, and with a control vector or HIP14, were metabolically labeled. Immunoprecipitated htt was analyzed as described above. (e) Palmitoylation was significantly (P = 0.03) increased in cells coexpressing wild-type htt and HIP14. In addition, HIP14 significantly (P = 0.02) increased palmitoylation of mutant htt. However, in the presence of HIP14, mutant htt was still significantly (P = 0.03) less palmitoylated than wild-type htt. (f) Cortical neurons transfected with GFP-tagged N548-128Q or N548-128Q(C214S), and with a control vector or FLAG-tagged HIP14, were labeled with the appropriate antibodies. The percentage of cells containing htt inclusions was significantly (P = 0.005) lower in the presence of HIP14 whereas no change was detected in the number of C214S inclusions, emphasizing the importance of HIP14 palmitoylation of htt in its distribution.
