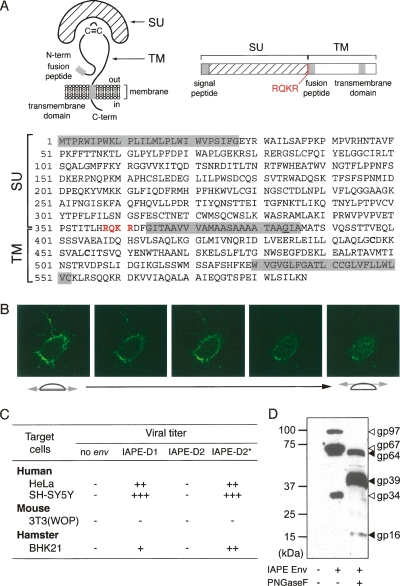
Figure 2.
Characterization of the IAPE Env glycoprotein. (A) Schematic structure and primary sequence of the IAPE-D1 Env protein. The SU and TM subunits are delineated, with the canonical furin cleavage site (R/K-X-R/K-R) between the two subunits indicated in red. The hydrophobic signal peptide, fusion peptide, and the transmembrane domain are shaded in gray. The G384 residue, mutated to E in the IAPE-D2 Env, is underlined. (B) Successive confocal images of a living cell stained for IAPE Env, demonstrating its localization at the cell surface. Human HeLa cells were grown on glass coverslips, transfected with the IAPE-D1 Env expression vector, and stained 48 h post-transfection, without permeabilization, with a rabbit anti-IAPE Env antiserum and an Alexa-Fluor 488-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody. (C) Infectivity assay of SIV particles pseudotyped with the IAPE-D Env proteins. Supernatants of human 293T cells cotransfected with an expression vector for the SIV core proteins, a lacZ gene-marked defective retroviral vector, and an expression vector for IAPE-D1, -D2, or -D2 E384G Env proteins (IAPE-D2*), or a control plasmid (no env) were used to infect human, murine, or hamster target cells. Viral titers, corresponding to the number of LacZ+ cell foci per milliliter of supernatant, are indicated as follows: (−) <10; (+) 10–100; (++) 100–1000; (+++) >1000. (D) Western blot analysis of SIV virions contained in the supernatant of transfected cells, pseudotyped (or not) with the IAPE-D1 Env protein. The corresponding samples from the infectivity assay in C were analyzed using a rabbit anti-IAPE Env antiserum. Supernatants were treated or not with peptide-N-glycosidase F (PNGaseF) as indicated.