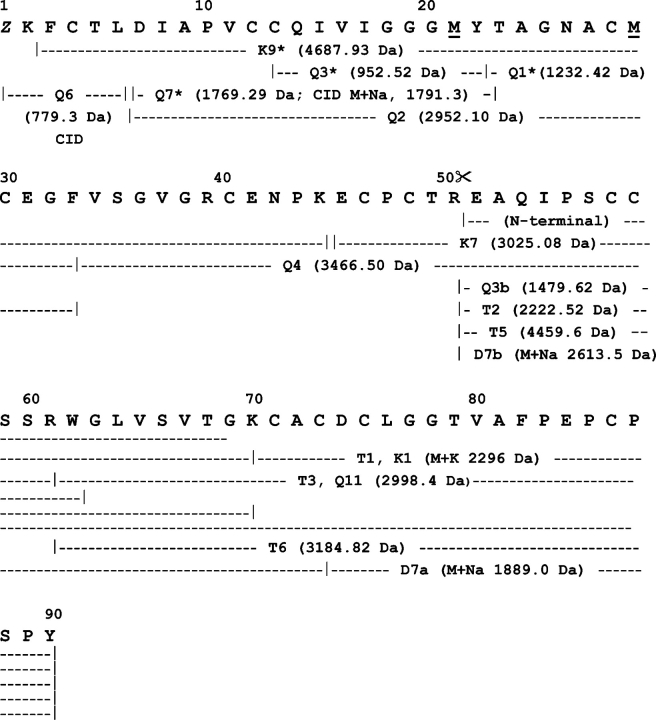
Figure 5.
Amino acid sequence of HML. The primary structure of HML was determined by combination of Edman degradation of sets of overlapping peptides obtained by proteolysis of the reduced and carbamidomethylated full-length lectin and its reversed-phase HPLC fragments (isolated as in Fig. 3 ▶) with chymotrypsin (Q-), trypsin (T-), endoproteinase Lys-C (K-), and endoproteinase Asp-N (D-), and by CID MS/MS analysis of the N-terminal blocked peptide Q76. Methionine residues at positions 21 and 29 were oxidized in peptides Q1 and K9, respectively. Proteolysis at the Arg50–Glu51 peptide bond, which generates the N-terminal sequence determined in the native two-chain HML lectin and in its 4460 C-terminal fragment (identical to peptide T5), is indicated by scissors. (Z) Pyroglutamic acid. Mass spectrometric sequence determination of Q6 is shown in Figure 6 ▶.