Figure 1.
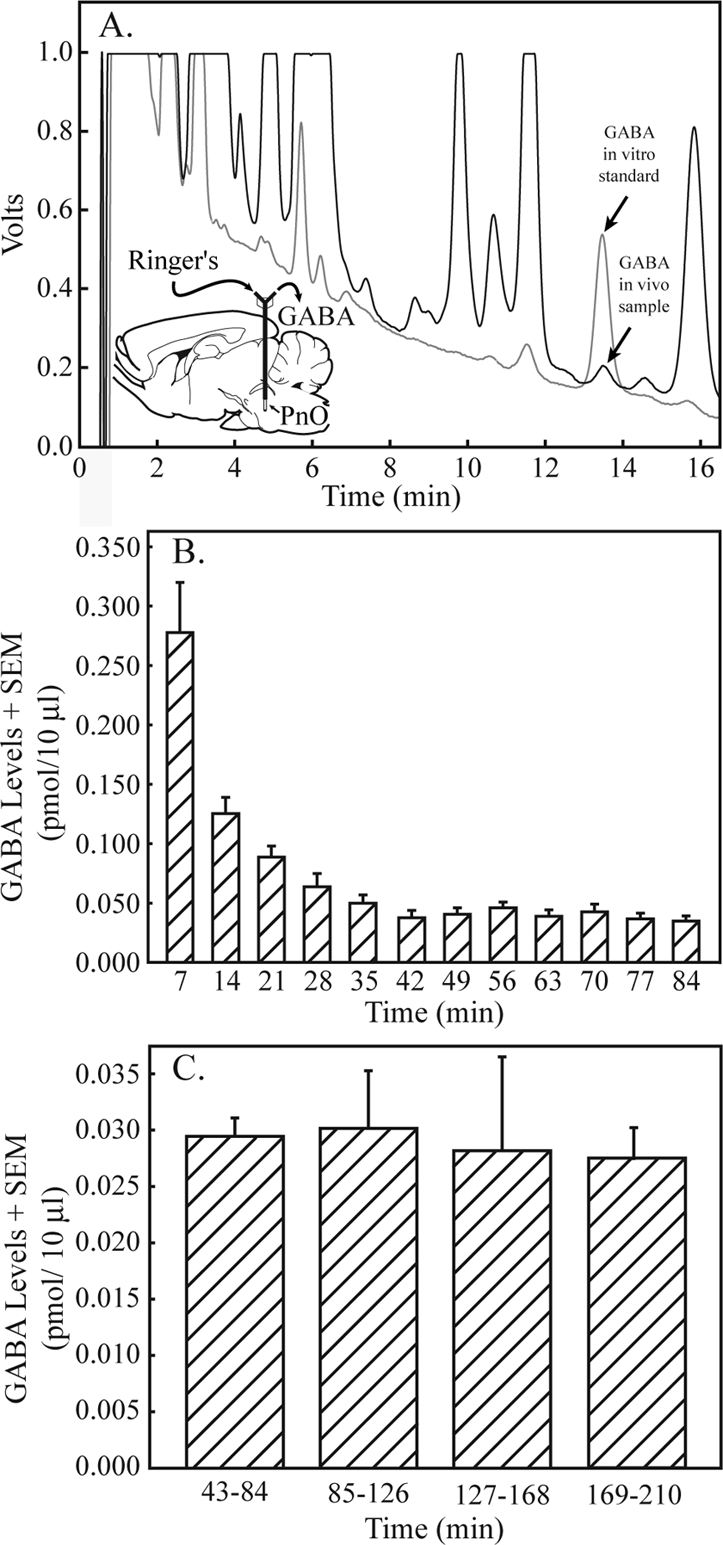
GABA levels in the pontine reticular nucleus, oral part (PnO) became stable by 42 minutes after dialysis probe insertion and remained stable for 2.8 hours. A. A representative chromatogram generated from a known quantity of GABA (in vitro standard, gray line, 0.913 pmol/10 μL) is shown superimposed on a typical chromatogram obtained by dialysis of the PnO (in vivo sample, black line; 0.107 pmol/10 μL), indicating the ability to identify GABA in brain samples. A sagittal diagram of the rat brain39 has been modified by adding a schematized microdialysis probe inserted in the PnO. The dialysis membrane at the tip of the probe is drawn to scale. Curved arrows indicate that Ringer solution was delivered to the probe through the inlet port and GABA from the PnO was collected at the outlet port. B. GABA levels in sequentially collected dialysis samples are plotted for the first 84 minutes after dialysis probe insertion into the PnO. Each bar indicates average GABA levels from 18 rats, plotted in 7 minute intervals. Thus, time 7 indicates minutes 1–7, and time 84 indicates minutes 78–84. C. GABA levels in the PnO remained stable for 2.8 hours of dialysis with Ringer solution. Each bar represents average PnO GABA levels in 18 dialysis samples (6 samples per rat x 3 rats).
