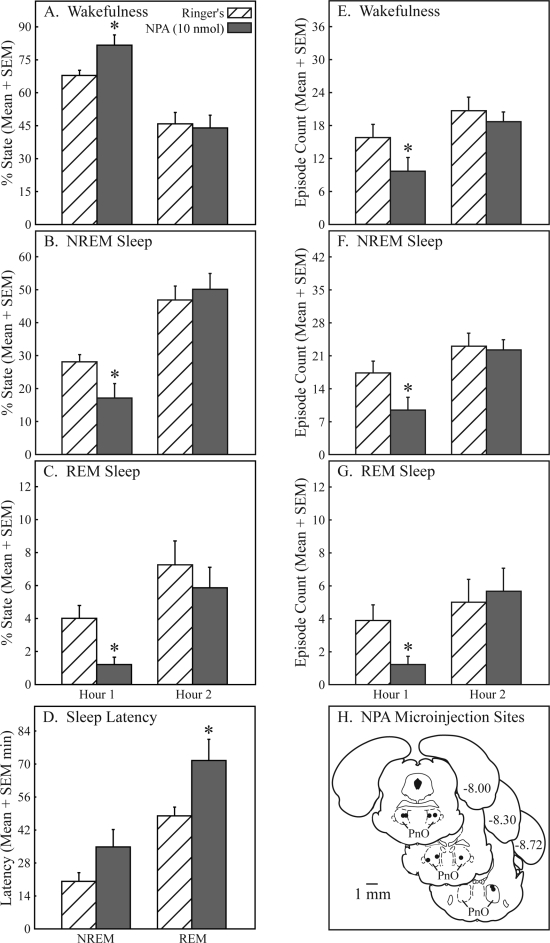
Figure 6.
Nipecotic acid significantly (*) increased wakefulness and decreased sleep in the first hour after microinjection into the pontine reticular nucleus, oral part (PnO). Nipecotic acid caused a 20% increase in wakefulness (A), a 39% decrease in non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep (B), and a 70% decrease in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep (C). Nipecotic acid also increased latency to onset of REM sleep by 49% (D). Nipecotic acid decreased the number of episodes of wakefulness (E, 39%), NREM sleep (F, 46%), and REM sleep (G, 68%). Nipecotic acid microinjection sites (H) were localized to the PnO and are represented by filled circles on 3 coronal diagrams modified from a rat brain atlas.39 Numbers at the right of each diagram indicate mm posterior to bregma. Sites where nipecotic acid was microinjected ranged from −7.82 to −8.73 mm from bregma.