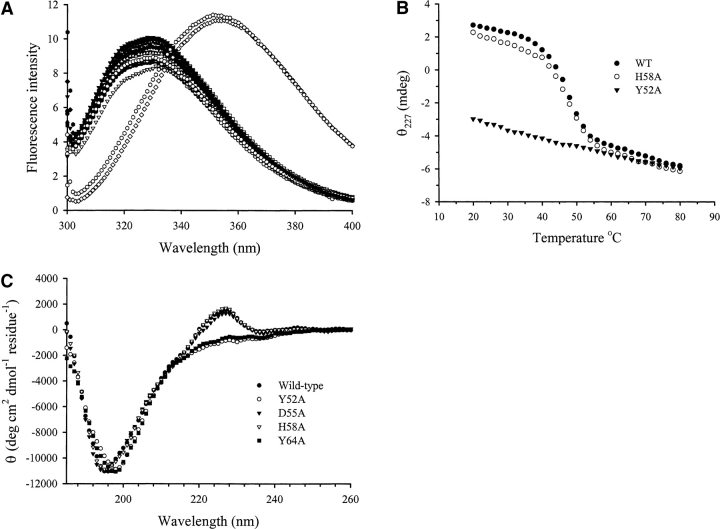
Figure 3.
Structural properties of purified mutant E3 rRNase domains probed by intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence and CD. (A) Tryptophan fluorescence emission spectra of wild-type and mutant rRNase domains. Fluorescence spectra (λex = 295 nm) were recorded at a protein concentration of 1 μM in 10 mM KPi (pH 7.0) at 25°C. All mutant rRNase domains except Y52A and Y64A displayed emission maxima of 330 (±1) nm, essentially identical to that of the wild-type protein. Y52A and Y64A rRNase show emission maxima of 354 nm, which is indicative of solvent-exposed tryptophan residues, indicating that these proteins are destabilized and do not possess a wild-type-like structure under these conditions. (B) Far-UV CD spectra of wild-type and mutant rRNase domains. (C) Thermal denaturation profiles of wild-type and mutant E3 rRNase domains. Comparison of thermal denaturation profiles for wild-type E3 rRNase, H58A, and Y52A monitored by the change in the far-UV CD signal at 227 nm.