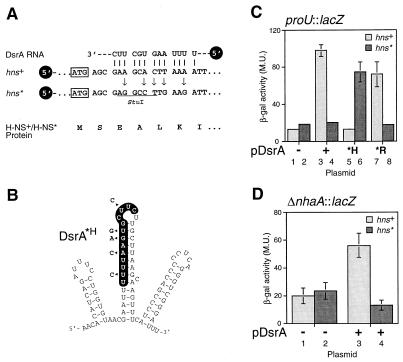
Figure 2.
DsrA acts via RNA:RNA interactions to repress H-NS. (A) Silent mutagenesis of hns to disrupt complementarity to DsrA. Five nucleotides of wild-type hns were modified by site-directed mutagenesis (arrows) to disrupt the DsrA:hns RNA base pairing (vertical lines). The mutations, which are silent in terms of the H-NS protein sequence (below), create a StuI restriction site (underlined) in the altered hns* allele. The initiator methionine codon is indicated (boxed). (B) DsrA mutations that prevent base pairing with hns but allow base pairing with hns*. Mutated nucleotides are shown next to the DsrA structure (arrowheads). (C and D) Assay of H-NS function in strains with and without hns RNA:DsrA complementarity. DsrA-induced repression of H-NS transcription silencing activity was assayed in strain M182 by using a proU∷lacZ (C) or ΔnhaA∷lacZ (D) reporter gene. β-galactosidase assays were performed as described (25), except that assays on ΔnhaA∷lacZ used a buffered growth medium (37). All assays were performed in duplicate; values given are the average of three independent experiments. Light columns, hns+ strains; dark columns, hns* strains. Plasmids used: −, pA vector; +, pDsrA; *H, pDsrA*H as in B; *R, pDsrA*R as in Fig. 3A.