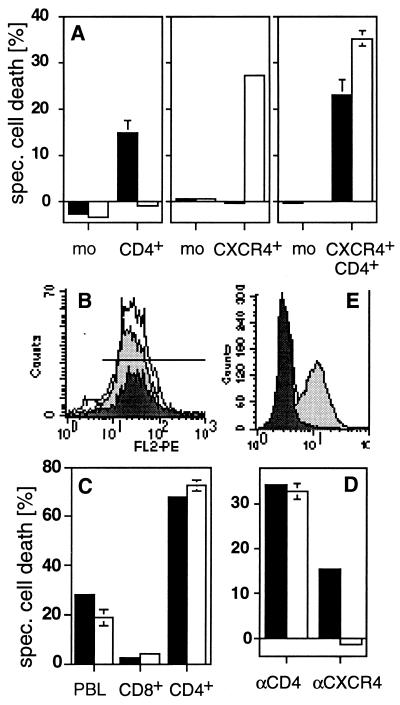
Figure 3.
CD4 and CXCR4 induce cell death independently of each other. (A) Anti-CD4-induced cell death (■) was observed in all CD4+ transfectants of the human B lymphoma cells tested. All CXCR4+ transfectants obtained were sensitive to anti-CXCR4-induced cell death (□). Double transfectants were sensitive to cell death induced by both mAbs. One representative example of every group of transfectants is shown. mean fluorescence intensity of CD4/CXCR4 of the clones used was: mock (3.85/2.57), CD4+ (47.12/2.56), CXCR4+ (4.03/65.7), and CD4+CXCR4+ (76.72/102.44). The killing assay was performed five times in triplicates as described in Materials and Methods. (B) CD8+ T cells (dark gray peak) express more CXCR4 than CD4+ T cells (light gray peak) (PBL = white peak). (C) Only CD4+ T cells are killed by anti-CD4 (■) and anti-CXCR4 (□) mAbs. Human PBL were sorted by negative selection with magnetic beads and cell death was induced. The experiment shown was done in triplicates and is representative of five independent experiments. (D) Down-regulation of CXCR4 by SDF-1 prevents anti-CXCR4- but not anti-CD4-induced cell death. HPB-ALL cells were preincubated in the absence (■) or presence (□) of 250 nM SDF-1 for 30 min at 37°C. The assay was performed in triplicates. One of five similar experiments is shown. (E) Down-regulation of CXCR4 was controlled by surface staining. White peak, control antibody; light gray peak, CXCR4 staining; dark gray peak, CXCR4 staining after preincubation with SDF-1 (24). Cell death in A, C, and D was determined by FSC/SSC analysis after 2 h.