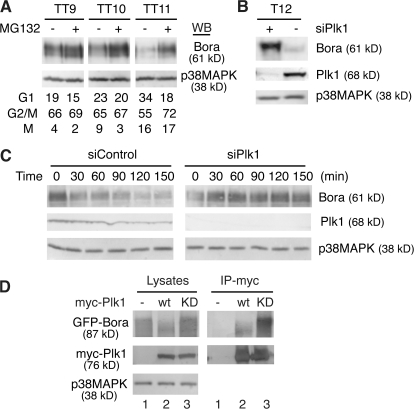
Figure 2.
Bora is degraded in a Plk1- and proteasome-dependent manner. (A) Proteasome-dependent degradation of Bora. HeLa S3 cells were synchronized with a double thymidine arrest and then released into fresh media. At 7, 8, and 9 h after release, the proteasome inhibitor MG132 or control DMSO was added and cells were collected 2 h later (TT9, 10, and 11, respectively). Protein levels were analyzed by Western blotting and cell cycle profile was determined by FACS. (B) Plk1 controls the Bora protein level. HeLa cells were transfected with a siRNA targeted to Plk1 (siPlk1) or a control siRNA, synchronized with thymidine for 18 h, and then released. At 10 h after release, 1 μM taxol was added and mitotic cells harvested 2 h later (T12). Protein levels were determined by Western blotting. (C) Plk1 controls Bora half-life. HeLa cells were synchronized by a double thymidine treatment and transfected with a control siRNA (siControl) or siPlk1 during the second thymidine arrest. At 8 h after release from the second thymidine arrest, 100 μg/ml cyclohexamine was added and cells were harvested at 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 150 min later. Half-life of Bora was determined by Western blotting. (D) Plk1 kinase activity is required for Bora degradation. GFP-Bora was cotransfected with a control vector (lane 1), myc-Plk1 (lane 2), or myc-Plk1-K82R (lane 3; KD, kinase dead) and cells were harvested at 48 h after transfection. Total cell lysates and the anti-myc immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting.