Figure 8.
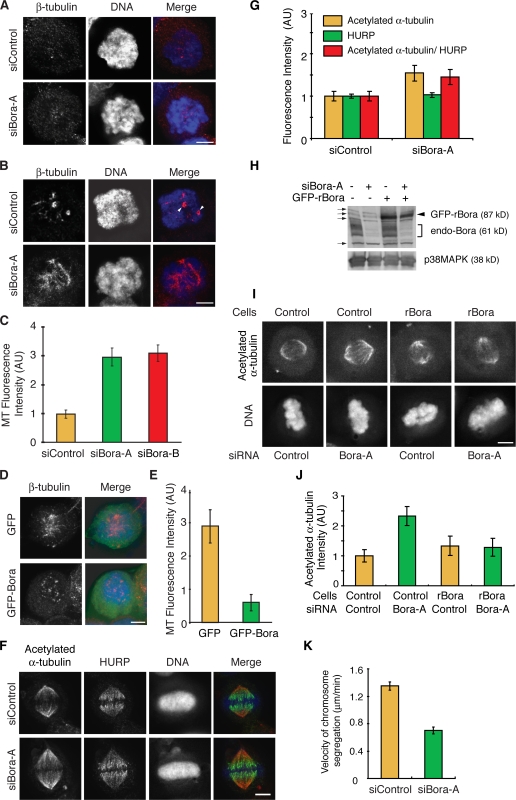
Bora controls spindle stability and microtubule growth in mitosis. (A–E) Shown in A, B, and D are maximum projections from deconvolved z stacks of representative HeLa cells stained for β-tubulin (red) and DNA (blue). Cells were transfected with siRNA (A–C) or with GFP/GFP-Bora (D and E). Transfected cells were treated with 5 μg/ml nocodazole for 10 min at 37°C, washed, released into fresh media, and fixed at 0 min (A) and 6 min (B–E) after release. Centrosomes are marked by arrowheads in B. Images from representative cells were acquired under constant exposure. The amounts of microtubules repolymerized at 6 min after release were quantified from 10 mitotic cells in each transfection and plotted in C and E. (F and G) Shown in F are maximum projections from deconvolved z stacks of representative control or Bora-depleted HeLa cells stained for acetylated α-tubulin (red), HURP (green), and DNA (blue). Images from representative cells were acquired under constant exposure. Mean HURP and acetylated α-tubulin immunofluorescence intensities on metaphase spindles was quantified (n = 20 half-spindles from 10 cells; G). Acetylated α-tubulin signal normalized against the HURP intensity of the same cell was also plotted. (H–J) Control and GFP-rBora–expressing HeLa cells were transfected with a control siRNA or with siBora-A and the knockdown efficiency was determined by Western blotting (H). Long exposure of Western blot uncovered cross reacting bands (H, arrows), one of which comigrated with GFP-rBora. The levels of acetylated α-tubulin were assayed by immunofluorescence staining (I), quantified, and plotted (J). (K) Velocity of sister chromatid segregation at anaphase A was measured in control and Bora knockdown cells from time-lapse movies shown in Fig. 7 (D and E; n = 32 anaphase cells for each quantification). AU, arbitrary units. Error bars show standard error. Bars, 5 μm.