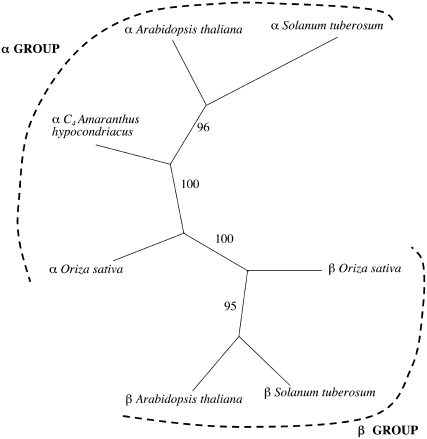
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of plant NAD-MEs. Mature proteins were aligned using the ClustalW (1.81) multiple alignment program (Thompson et al., 1994), and the alignment obtained was modified by visual inspection to exclude the sites containing gaps. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method using the Phylip software package (Felsenstein, 1989). Statistical significance of each branch of the tree was evaluated by bootstrap analysis by 100 iterations of bootstrap samplings and reconstruction of trees by the neighbor-joining method. The topology obtained by this method is shown along with statistical significance of each branch. The following sequences are included: α-subunits from A. hypochondriacus (U01162; photosynthetic NAD-ME), Arabidopsis (At2g13560), potato (Z23023), and Oryza sativa (NM_001066235), and β-subunits from Arabidopsis (At4g00570), O. sativa (NM_001071533), and potato (Z23002).