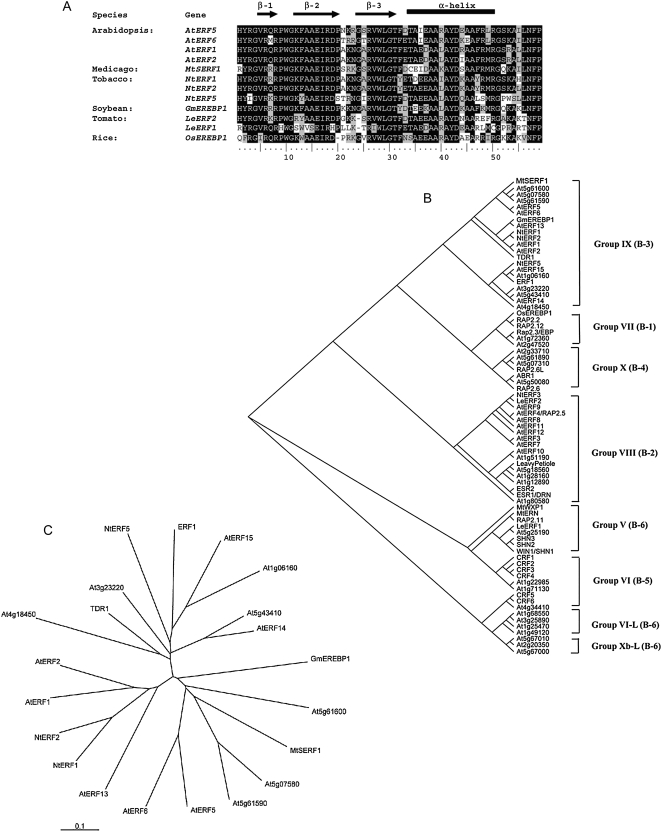
Figure 11.
A, Alignment of the AP2/ERF domain of M. truncatula MtSERF1 with AP2/ERF domains from other plant species. Sequences were aligned with ClustalW implemented in ClustalX (1.8) using default parameters. Black and gray shading of the residues indicates identical and similar amino acid residues, respectively. Gaps required for optimal alignment are indicated by dashes. The black bar and arrows represent predicted α-helix and β-sheet regions, respectively, within the AP2/ERF domain (Allen et al., 1998). B, An unrooted cladogram of MtSERF1 and all known members of the ERF subfamily of Arabidopsis and other well-characterized genes from other species. The names of the genes were given when they are well characterized; otherwise, they are presented as TIGR ID. The tree was generated using the neighbor-joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987) on ClustalX 1.8 software. Groups were named according to Nakano et al. (2006). Classification by Sakuma et al. (2002) is indicated in parentheses. The analysis is based on the amino acid sequences of the AP2/ERF domain. C, An unrooted phylogenetic tree of MtSERF1 and ERFs clustered in Group IX, using the entire amino acid sequence. Branch lengths are drawn to scale. Bar is estimated amino acid substitutions per site.