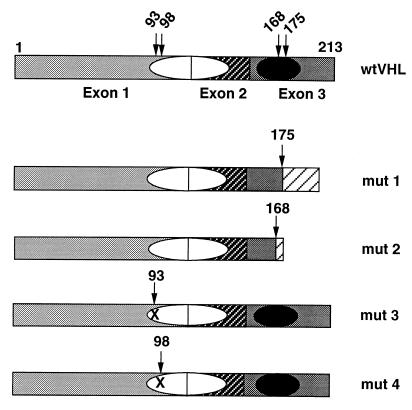
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the domain structure of wt and naturally occurring mut pVHLs. The three exons are indicated by different shadowing; the putative protein binding domains are represented by ovals, the filled one is the elongin binding domain; numbers above the pictures are amino acid residues, arrows indicate residues involved in producing mut pVHLs. Mut 1 is a 1-bp deletion creating a frameshift after residue 175; mut 2 is a 4-bp insertion creating a frameshift after residue 168; mut 3 and mut 4 are missense mutations, Gly-93–Asp and Tyr-98–His, respectively. Mut 1 and mut 2 are devoid of the elongin binding domain; mut 3 and mut 4 possess an intact functional elongin binding domain.