Figure 4. Correlation of tracer accumulation and αvβ3 expression.
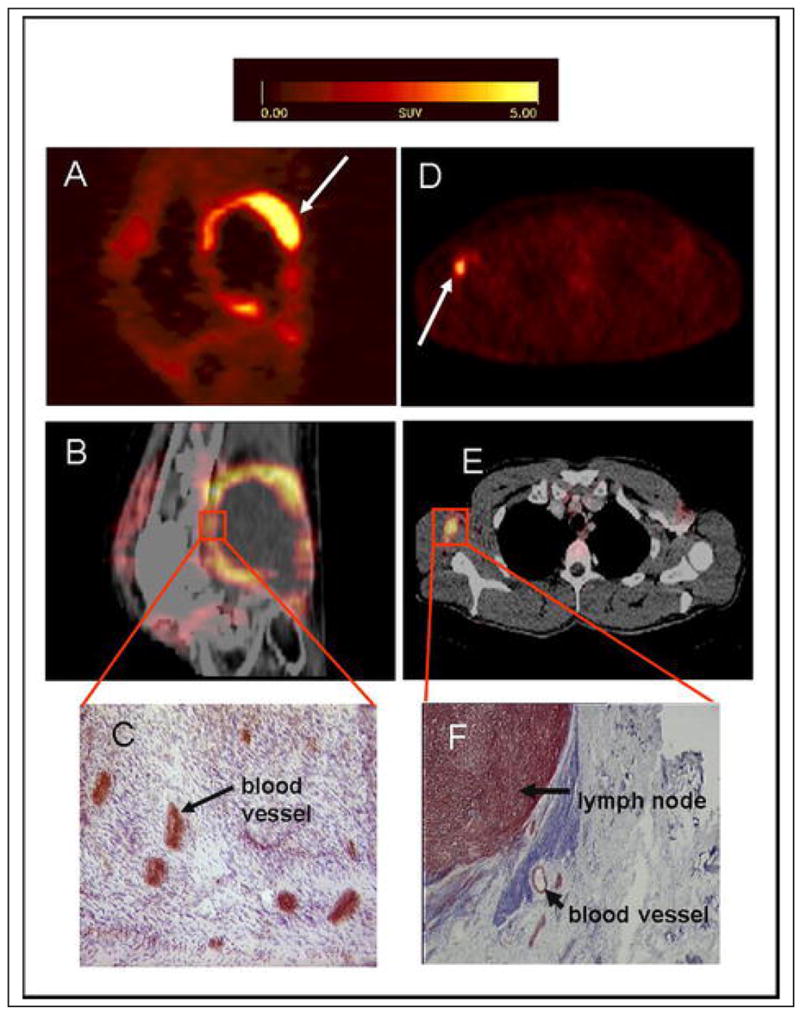
(A–C) patient with a soft tissue sarcoma dorsal of the right knee joint. (A) The sagittal section of a [18F]galacto-RGD PET acquired 170 min p. i. shows circular peripheral tracer uptake in the tumor with variable intensity and a maximum SUV of 10.0 at the apical-dorsal aspect of the tumor (arrow). (B) The image fusion of the [18F]galacto-RGD PET and the corresponding computed tomography scan after intravenous injection of contrast medium shows that the regions of intense tracer uptake correspond with the enhancing tumor wall, whereas the non-enhancing hypodense center of the tumor shows no tracer uptake. (C) Immunohistochemistry of a peripheral tumor section using the anti-αvβ3 monoclonal antibody LM609 demonstrates intense staining predominantly of tumor vasculature. (D–F) patient with malignant melanoma and a lymph node metastasis in the right axilla. (D) The axial section of a [18F]galacto-RGD PET acquired 140 min p. i. shows intense focal uptake in the lymph node (arrow). (E) Image fusion of the [18F]galacto-RGD PET and the corresponding computed tomography scan after intravenous injection of contrast medium. (F) Immunohistochemistry of the lymph node using the anti-αvβ3 monoclonal antibody LM609 demonstrates intense staining predominantly of tumor cells and also blood vessels.
From: Noninvasive Visualization of the Activated αvβ3 Integrin in Cancer Patients by Positron Emission Tomography and [18F]Galacto-RGD Haubner R, Weber WA, Beer AJ, Vabuliene E, Reim D, et al. PLoS Medicine Vol. 2, No. 3, e70 doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020070
