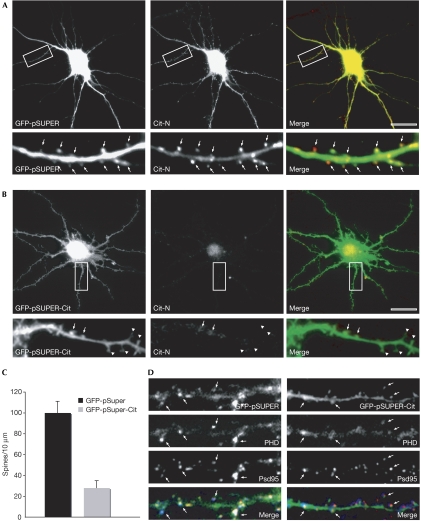
Figure 2.
Citron-N knockdown results in a decreased density of mature spines. Cultured hippocampal neurons (21 DIV) were transfected with (A) a control green fluorescent protein (GFP)-pSuper vector or (B) a GFP-pSuper-Cit-N short-interfering RNA construct. Two days after transfection, cells were processed for immunofluorescence microscopy with Cit-N antibodies. The arrows indicate Cit-N immunoreactivity associated with mature spines, whereas the arrowheads indicate immature dendritic protrusions. (C) Quantitative analysis of the linear density of mushroom spines in dendrites of control cells compared with RNA interference-treated cells. Error bars, standard error; P<0.01, Student's t-test. (D) High-magnification images of dendrites from a 21 DIV PHN treated as in panels (A) and (B), respectively, stained with Psd95 antibodies (red) and phalloidin (PHD; blue). The arrows indicate the colocalization of Psd95/actin. Cit-N, Citron-N; DIV, days in vitro; PHN, primary hippocampal neuron. Scale bar, 10 μm.