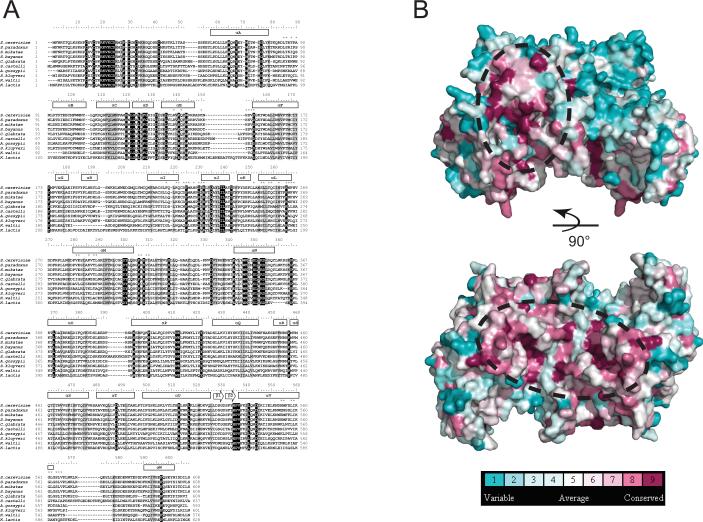
Figure 3. Evolutionary conservation of Cep3p.
A. Multiple sequence alignment of Cep3p orthologs from ten point centromere-containing fungi. The alignment is numbered according to the S. cerevisiae Cep3p sequence. Secondary structural elements are indicated above the alignment. Residues participating in dimer contacts are indicated by asterisks above the alignment. Shaded boxes indicate conserved (gray) and invariant (black) residues. B. Side view and bottom view of the Cep3p dimer molecular surface colored by degree of conservation. The dotted ovals indicate two regions of high conservation that may represent Ctf13p interaction surfaces. Residues on the apex are highly variable, and they are presumably not involved in conserved protein-protein contacts.