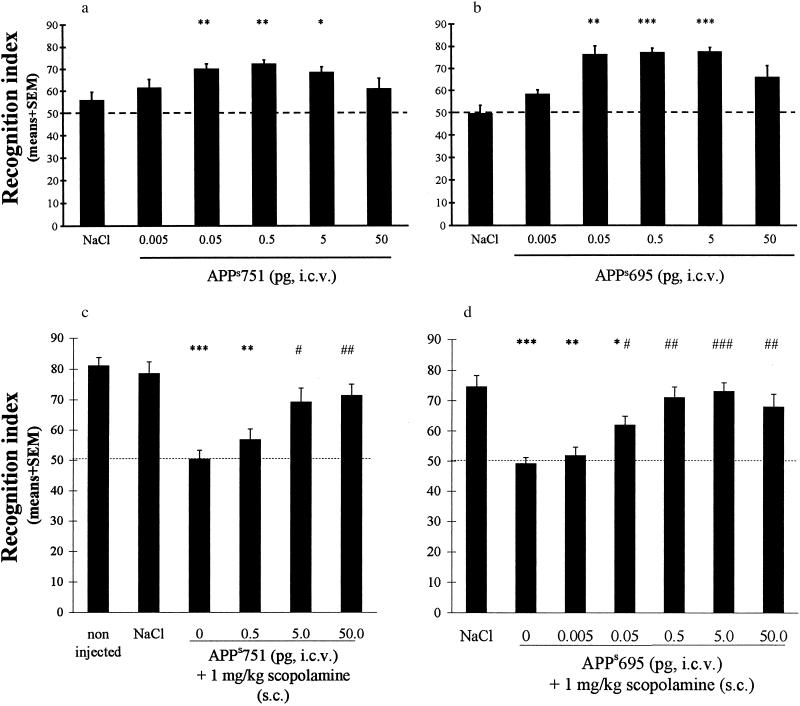
Figure 3.
APPs751 and APPs695 improve retention performance and block retention deficits induced by scopolamine in an object recognition task. When using a 24-hr delay, both APPs751 and APPs695 (a and b, respectively) dose-dependently (0.05–5 pg) improve retention performance. When using a 3-hr delay, both APPs751 and APPs695 (c and d, respectively) block retention deficits induced by scopolamine (1 mg/kg). In each experiment, the recognition index significantly differed among groups [Kruskall-Wallis test: (a) H = 15.19, P < 0.01; (b) H = 29.96, P < 0.0001; (c) H = 34.39, P < 0.0001; (d) H = 37.52, P < 0.001]. ∗, P < 0.05, ∗∗, P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗, P < 0.001 vs. saline, and #, P < 0.05, ##, P < 0.01, and ###, P < 0.001 vs. scopolamine, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.