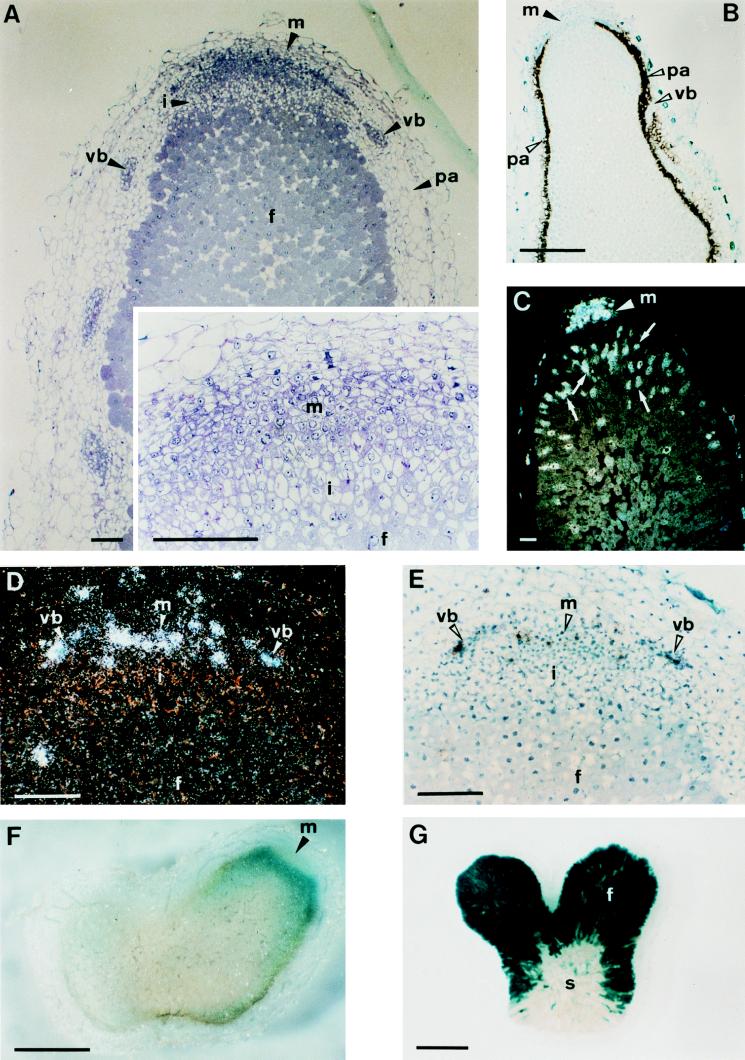
Figure 2.
Zonation of indeterminate 30-day-old Sesbania rostrata nodules. (A) Longitudinal, 2-μm section of a nodule embedded in Technovit and stained with toluidine blue. The Inset is a magnification of the apical part. (B) Bright-field image of an in situ hybridization with a SrEnod2 antisense probe in a 10-μm longitudinal section. Silver grains are seen as black dots. (C) Dark-field image of an in situ hybridization with a histone H4–1Sr antisense probe. Silver grains are seen as white dots. (D and E) Dark- and bright-field images of an in situ hybridization with a Sesro;CycB1;1 antisense probe. (F) Section (100-μm) of a β-glucuronidase-stained nodule induced by Azorhizobium caulinodans ORS571 (pRG960SD-32) harboring a plasmid with a nodA-gusA fusion. (G) β-Galactosidase-stained 100-μm section of a nodule induced by A. caulinodans ORS571 (pRG2002) harboring a plasmid with a nifH-lacZ fusion. Arrowheads indicate the different nodule tissues and hybridization signals and arrows (C) point out cells with endoreduplication. Abbreviations: f, fixation zone; i, invasion zone; m, meristem; pa, nodule parenchyma; s, senescence zone; vb, vascular bundle. [Bars = 100 μm (A and C–E) or 1 mm (B, F, and G).]