Figure 1.
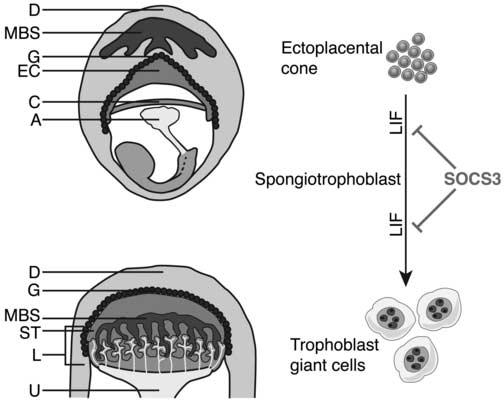
Precursor trophoblast cells within the ectoplacental cone (EC) mature to form the spongiotrophoblast layer of the placenta. Diagrammatic representation of an E8 embryo and extraembryonic tissues within the maternal decidua (top) and an E10 placenta (bottom). The spongiotrophoblast layer lies between the outer secondary trophoblast giant cells and the inner labyrinthine layer. (Some trophoblast giant cells may arise from a cell type within the ectoplacental cone that does not express spongiotrophoblast markers [not shown] (Simmons and Cross, 2005). LIF acts to promote differentiation of trophoblasts to giant cells and SOCS3 negatively regulates signalling downstream of LIF. A, allantois; C, chorionic plate; D, decidua; EC, ectoplacental cone; G, trophoblast giant cells; L, labyrinth; ST, spongiotrophoblast; U, umbilicus; MBS, maternal blood supply
