Figure 3. The decay kinetics of NMDA receptor EPSCs in axotomised motoneurons.
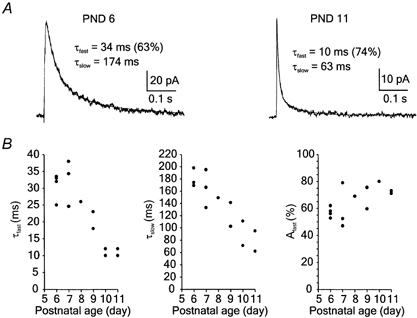
A, examples of EPSCs (6 responses were averaged in both cases) evoked in motoneurons of a 6-day-old (PND 6) and an 11-day-old animal (PND 11). The decay of NMDA receptor EPSCs was fitted by a double exponential function with the time constants and their relative amplitude indicated. Note the differences in the decay kinetics of NMDA receptor EPSCs. EPSCs were recorded from motoneurons at a holding potential of +40 mV in the presence of 1 mm Mg2+ and 5 μm CNQX. B, the graphs indicate the fast component (τfast), the slow component (τslow) and the relative contribution of the fast component (Afast) of the NMDA receptor EPSC in axotomised motoneurons. The values of the fast and slow components of NMDA receptor EPSCs in motoneurons of PND 6–11 significantly decreased as a function of time after axotomy (one-way ANOVA; Pfast = 0.0015; Pslow = 0.0035); however, the relative contribution of these components was not significantly changed (P = 0.185).
