Figure 8. Modification of hH1 and μ1 channels in 65 mm external and 10 mm internal sodium solutions.
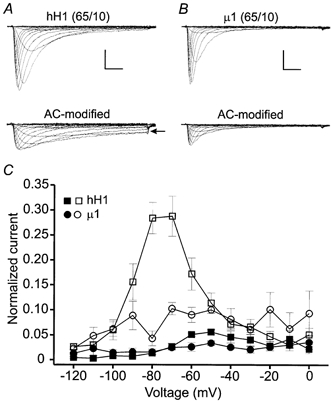
Under these conditions the channels were modified by perfusing the cells with external solution containing 100 μm AC and delivering 100 pulses to −30 mV. A, hH1 current traces before (upper) and after (lower) channel modification by external perfusion of 100 μm AC. AC modification elicited sustained inward currents (arrow) at voltages near the activation threshold. B, μ1 current traces before and after AC modification. Scale in A and B, 2 nA, 2 ms. C, normalized measures of sustained inward currents in 65 mm external and 10 mm internal sodium solutions. The data were normalized as described in Fig. 7B and C. In control saline, the amplitudes of hH1 (n = 4) and μ1 (n = 3) currents at the end of the voltage step commands were ≤ 5 % of the peak inward current. AC modification of hH1 channels (□) elicited a sustained inward current at −80 and −70 mV that was 28 % of the peak inward current (n = 4); the largest sustained inward current of AC-modified μ1 channels (○) was 10 % of the peak inward current and occurred during a voltage step to −70 mV (n = 3).
