Figure 4. Effects of Rp-cAMPS on L-type Ca2+ current amplitude and steady-state inactivation.
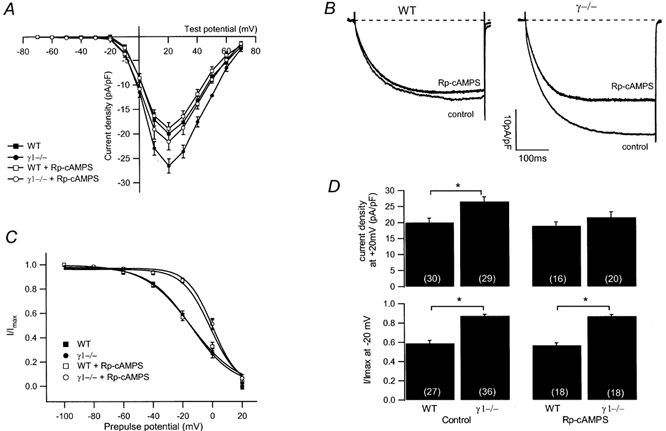
A, averaged I-V relationships in the presence and absence of 100 μm Rp-cAMPS from WT (filled squares, without Rp-cAMPS, n = 30; open squares, with Rp-cAMPS, n = 17) and γ1-deficient (filled circles, without Rp-cAMPS, n = 29; open circles, with Rp-cAMPS, n = 20) myotubes. B, representative current traces at +20 mV in the absence (control) or presence of 100 μm Rp-cAMPS from a WT and a γ1-deficient myotube. Traces of WT and γ1-deficient cells in the absence of Rp-cAMPS same as in Fig. 1A,C, normalised steady-state inactivation for WT (filled squares, n = 27) and γ1-deficient cells (filled circles, n = 36) under control conditions and in the presence of Rp-cAMPS (100 μm) (WT, open squares, n = 18; γ1−/−, open circle, n = 18). D, bar graph summarising the effect of 100 μm Rp-cAMPS on the current density at +20 mV (top) and on the steady-state inactivation after a prepulse of −20 mV (bottom) for WT and γ1-deficient myotubes. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (P < 0.05), values in parentheses indicate number of cells.
