Figure 9. Whisker-evoked IPSPs are suppressed by thalamic activation.
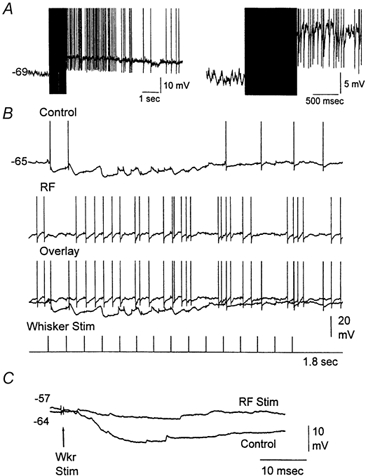
A, example of an intracellular recording from a VPM neuron showing the effect of stimulating the brainstem reticular formation (100 Hz, 1 s). The right trace is a close-up. B, the neuron responded to whisker stimulation (15 stimuli, 10 Hz) with robust IPSPs that hyperpolarized the cell during the initial sensory stimuli (control). Thalamic activation produced by stimulating the brainstem reticular formation blocked the sensory-evoked IPSPs in the VPM neuron (RF). Action potentials are truncated. C, IPSP evoked by a single whisker stimulus delivered before (Control) and after RF stimulation. Both traces are overlaid for comparison. The membrane potential values for the beginning of each trace (before the whisker stimulus) are displayed.
