Figure 7. Calcium dependence of contraction and its inhibition by nifedipine.
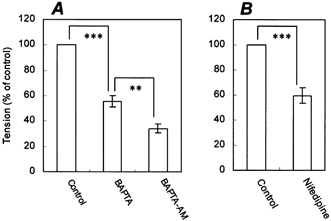
A, the first contraction was induced by adding 100 μm ACh (control) in normal Hepes-buffered Tyrode solution. The fibre was then washed for 60 min with calcium-free, Hepes-buffered Tyrode solution. The second contraction was induced by adding 100 μm ACh in calcium-free solution in the presence of 1 mm BAPTA, an extracellular Ca2+ chelator (BAPTA). The fibre was then washed for 60 min with calcium-free solution and treated with 50 μm BAPTA-AM, an intracellular Ca2+ chelator. The third contraction was induced by adding 100 μm ACh (BAPTA-AM). B, the first contraction was induced by adding 100 μm ACh (control). The fibre was then washed for 60 min and treated with 3 μm nifedipine for 10 min. The second contraction was induced by adding 100 μm ACh (nifedipine). The data are expressed as percentages of the first contraction. Bars represent means ± s.e.m. (n = 4). **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.005, compared between groups.
