Figure 4. Block of KCNQ channels reduces the tail current.
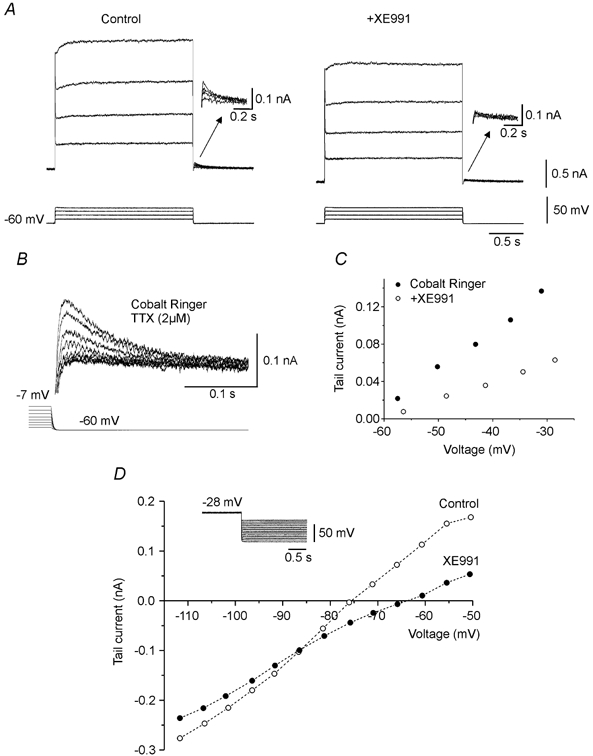
In voltage clamp, addition of XE991 (1 μm) reduced the voltage-sensitive tail current (arrows in A). A similar voltage-sensitive tail current present in cobalt Ringer (B and C) was reduced by XE991 (5 μm) (C). B and C are from different motoneurones. The ionic basis of the XE991 sensitive current was investigated by applying hyperpolarized voltage steps of increasing amplitude (protocol illustrated in D) in the presence of ZD 7288 (100 μm). The amplitude of the tail current was measured as a function of the potential before and after addition of XE991 (5 μm) (D). The 2 curves were crossing at −86 mV, value which indicates the reversal potential for ions carrying the tail current. Action potentials were blocked by TTX. A and D in the presence of nifedipine.
