Figure 1. Acidosis-stimulated medullary raphe neurones responded to changes in pHo induced either by changes in PCO2 or in [NaHCO3]o.
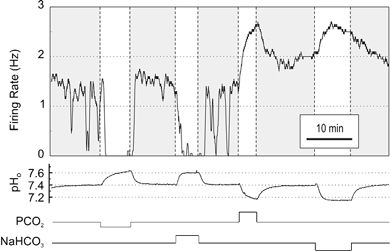
Shown is a neurone that increased its firing rate in response to both hypercapnic acidosis and isocapnic acidosis, and decreased its firing rate in response to both hypocapnic alkalosis and isocapnic alkalosis.
