Figure 5. Acidosis-stimulated raphe neurones responded to changes in pH in the absence of CO2 and bicarbonate.
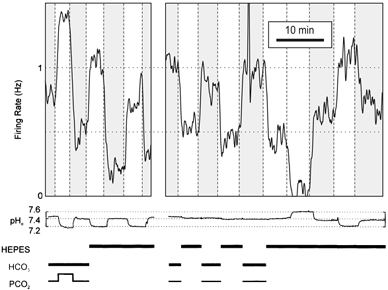
This neurone increased its firing rate in response to hypercapnic acidosis, and also responded to changes in pH in Hepes-buffered solution. When switching between normal Ringer solution (pH 7.4, PCO2 5 %) and Hepes-buffered solution (pH 7.4, PCO2 0 %), the neurone responded as other acidosis-stimulated neurones did to isohydric hypocapnia. Bars at bottom depict the presence or absence of Hepes, CO2 and bicarbonate.
