Figure 5. Effect of linopirdine on the resting membrane potential and on the membrane potential response to prolonged application of histamine.
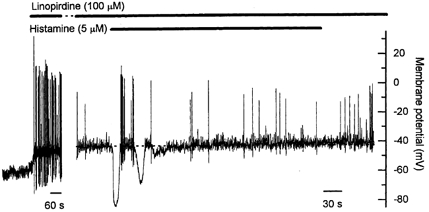
Linopirdine (100 μm), an inhibitor of M-channels, caused a rapid depolarization of the resting membrane potential that was associated with an increase in the frequency of action potentials. The initial histamine-induced hyperpolarization persisted in the presence of linopirdine, but the sustained depolarization was markedly reduced in amplitude. The increase in action potential frequency was not observed, though this may be in part due to non-specific effects of linopirdine (see Results for details). The gap represents 11 min. Note the different time scales in the two parts of the figure.
