Figure 6. Time course of GABAAR- and glyR-mediated inhibition.
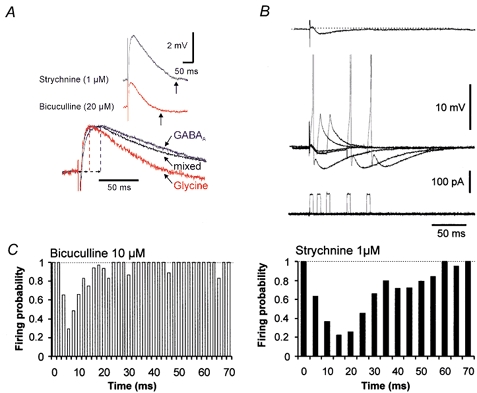
A, kinetics of evoked GABAAR- and glyR-mediated IPSPs recorded with a pipette containing 22 mm Cl−. Vertical arrows indicate the end of the IPSP. Lower traces, scaled glyR-mediated, mixed, and GABAAR-mediated IPSPs. B, protocol for assay of the time window of inhibition by pharmacologically isolated IPSPs recorded with a pipette containing 4 mm Cl−. Single APs were elicited by brief (5 ms) current injections delivered 5-10 times with variable delays after synaptic stimulation (steps of 2 and 5 ms for glyR- and GABAAR-mediated IPSPs, respectively). Typically, the time course of the glycinergic IPSP was determined first since strychnine displayed poor wash out. The recovery of the GABAergic IPSP was usually obtained within 5-10 min of the wash out of bicuculline. The stability of recording was monitored by eliciting, alternately, single APs without synaptic stimulation (not shown). AP generation was inhibited when the depolarizing current pulse was delivered at the peak of the IPSP. C, left, time course of the inhibitory power of glyR-mediated IPSPs (n = 3). The peak of inhibition (firing probability of 0.29 ± 0.18) was obtained at 6 ms. Right, time course of the inhibitory power of GABAAR-mediated IPSPs (n = 3). The peak of inhibition (firing probability of 0.22 ± 0.11) was obtained at 15 ms.
