Figure 1. R-R interval and systolic pressure power in 20 healthy young subjects in the supine and 40 deg tilt positions with and without fixed rate atrial pacing.
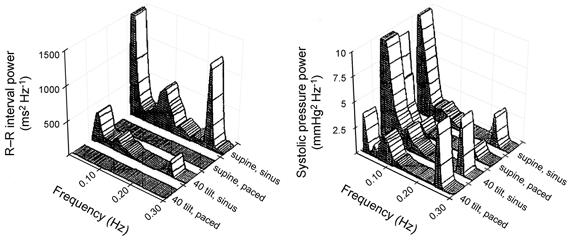
Elimination of R-R interval variability significantly reduces pressure oscillations at the respiratory frequency in supine humans, but increases them in the 40 deg tilt position. Moreover, it has no effect on Mayer wave (≈0.1 Hz) pressure oscillations in supine humans, but increases them in the 40 deg tilt position. This demonstrates the frequency and state dependence of cardiovascular oscillations (modified from Taylor & Eckberg, 1996).
