Figure 5. Role of the hydrophobic tail and polar head in inhibition of VDACL currents by arachidonic acid.
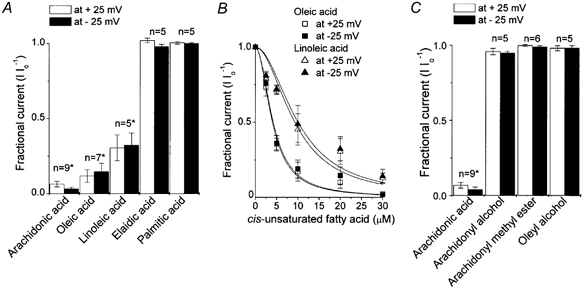
A, relative effects of cis-unsaturated (arachidonic, oleic and linoleic), trans-unsaturated (elaidic) and saturated (palmitic) fatty acids (all 20 μm) on macropatch currents recorded in the inside-out mode at ±25 mV. * Significantly different from control at P < 0.001. B, concentration-dependent inhibition of macropatch currents by oleic acid (squares) and linoleic acid (triangles). Open symbols are data for +25 mV and filled symbols are for −25 mV (mean ± s.e.m.). The data were fitted to eqn (1) with Kd / 4.02 ± 0.21 μm for +25 mV and Kd = 4.19 ± 0.34 μm for −25 mV in the presence of oleic acid, and Kd = 9.3 ± 1.2 μm for +25 mV and Kd = 10.0 ± 1.3 μm for −25 mV in the presence of linoleic acid (n = 5-7). The Hill coefficient was 2. C, effects of non-charged arachidonic acid analogues, arachidonyl alcohol and methyl ester, and a non-charged oleate analogue, oleyl alcohol, on VDACL macropatch currents in inside-out patches. Data were normalized to the mean current measured before application of drugs (Io).
