Figure 4. Effects of voluntary ADM contraction compared to rest on paired-pulse TMS measures of motor excitability.
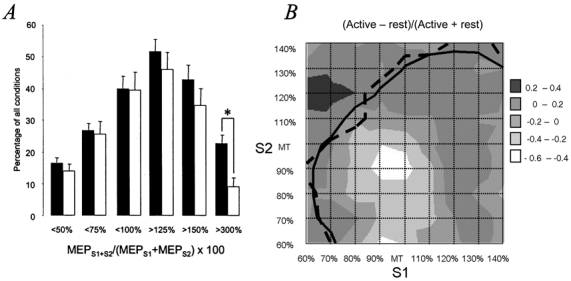
A, number of conditions (given as percentage of all 81 conditions, y-axis) below or above discrete interaction levels of (MEPS1+S2/MEPS1 + MEPS2) × 100 as indicated on the x-axis. ▪ and □, resting and active ADM before DZP intake, respectively. Data are from the seven subjects who participated in both experiments. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Note that voluntary contraction did not affect SICI but resulted in a significant decrease in the highest SICF level. *P < 0.01. B, mean weighted differences (n = 7 subjects) of each condition of S1 and S2 comparing the paired-pulse interaction (MEPS1+S2/MEPS1 + MEPS2) in the active and resting ADM. The continuous and dashed lines are the (MEPS1+S2/MEPS1 + MEPS2) × 100 = 100 % contour lines at rest and during contraction, respectively, to delineate SICI and SICF ‘areas’. Note that contraction decreased the highest values of SICF but did not result in a shift of the 100 % contour line.
