Figure 1. Whole-cell currents and current-voltage relationships for wild-type (WT) and Q552R human voltage-gated skeletal muscle chloride channels (hClC-1 channels) expressed in tsA201 cells.
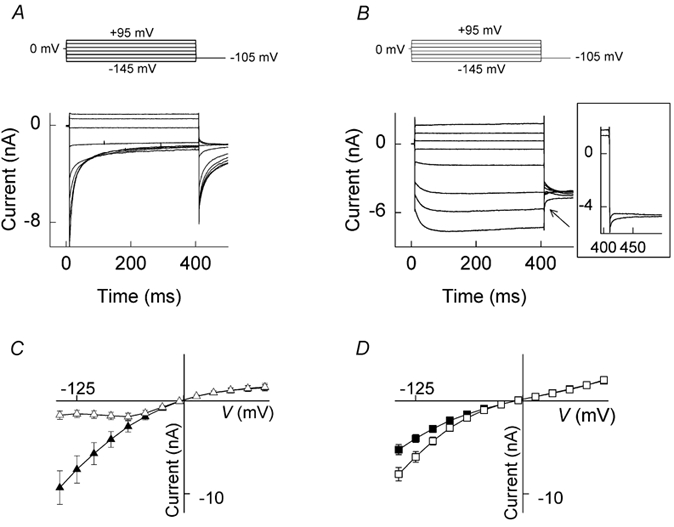
From a holding potential of 0 mV, currents were elicited in 20 mV intervals over the voltage range −145 to +95 mV followed by a fixed pulse of −105 mV for 90 ms. A, current traces from a cell expressing WT hClC-1 channels. B, current traces from a cell expressing Q552R hClC-1 channels (only alternate current traces are shown for clarity). The arrow points to a tail current deactivation following current activation at +95 mV. The inset shows the tail currents following pulses of +75 and +95 mV. C and D, the voltage dependence of the instantaneous (filled symbols) and late (open symbols) current amplitudes for WT and Q552R hClC-1 channels, respectively. Mean values ± s.e.m. are given for n = 6 (WT) and n = 15 (Q552R) cells.
