Figure 7. Diazo-2-induced relaxation at 15 °C in skinned psoas fibres with endogenous TnC, rTnC or mutant TnC in standard solution.
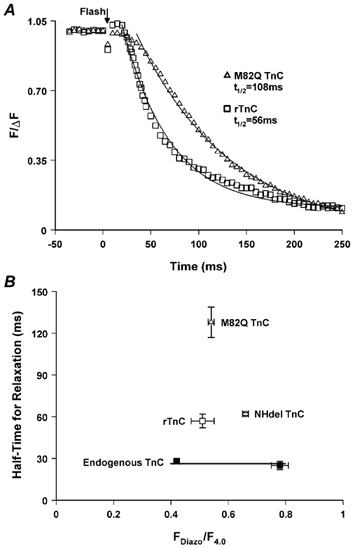
A, examples of relaxation in fibres reconstituted with rTnC (□) or M82Q TnC (▵). To emphasize the kinetics of relaxation, force has been normalized to the extent of relaxation, ΔF. Relaxation was induced at similar pre-photolysis force (Fpre/F4.0 = 0.48 for rTnC and 0.53 for M82Q TnC) and similar chelating capacity (2440 for rTnC and 3238 for M82Q TnC) and resulted in a similar post-photolysis force (Fpost/F4.0 = 0.08 for rTnC and 0.05 for M82Q TnC) but a slower rate of relaxation in the presence of M82Q TnC. B, mean half-relaxation time (t1/2) values are plotted as a function of relative force for fibres containing different forms of TnC. Relaxation was induced at similar chelating capacities: endogenous TnC (▪) 2880, rTnC (□) 2440, M82Q TnC (▵) 3238 and NHdel TnC (○) 3082. See Table 3 for further details.
