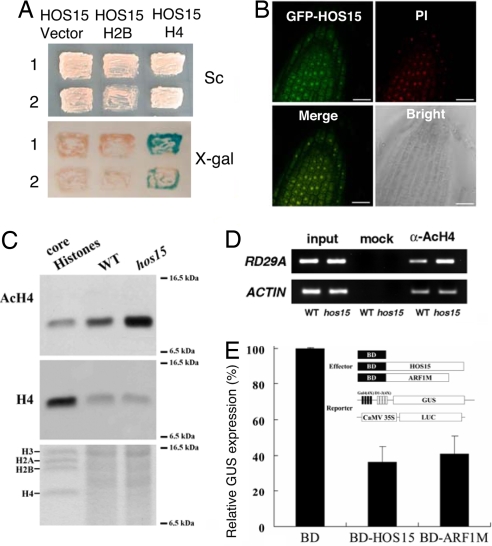
Fig. 5.
HOS15 is important for histone deacetylation. (A) (Upper) two independent yeast cotransformant strains carrying both of HOS15 and vector control (Left), HOS15 and H2B (Center), and HOS15 and H4 (Right) were streaked onto selective media. (Lower) activation of the lacZ reporter gene is indicated by the formation of blue colonies on plates containing X-Gal. (B) Confocal microscope images of root tip cells of transgenic plants transformed with GFP-HOS15 construct. Propidium iodide (PI) staining indicates the positions of nuclei. (C) Western blot analysis with anti-acetylated H4 antibody (Top) revealed that hos15 plants accumulate elevated levels of acetylated H4 compared with WT. Core histones were used as immunoblot control. Western blot, using anti-H4 antibody (Middle) and Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining (Lower) indicate equal amount of proteins were loaded. (D) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis, using antibody recognizing actylated histone H4 (α-AcH4). RD29A promoter DNA associated with immunoprecipitated histone was amplified by PCR. Actin served as an internal control. Input: rescued genomic DNA before adding anti-AcH4 antibody (α-AcH4). Mock: ChIP without anti-α-AcH4 antibody. (E) HOS15 functions as a transcriptional repressor. Arabidopsis leaf protoplasts were cotransfected with a reporter gene and two effector genes. Effector genes containing yeast Gal4 DBD (BD) fused in-frame with either HOS15 or ARF1M (control).