Fig. 1.
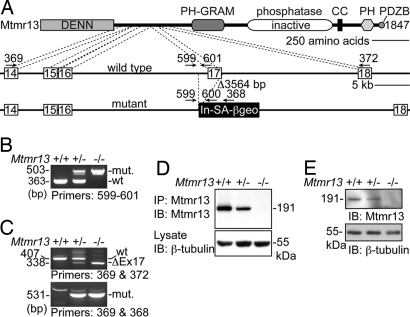
Disruption of Mtmr13. (A) A representation of the manner in which Mtmr13 is disrupted in ES cell line RRF511. The Mtmr13 protein is depicted with indicated protein domains. Cell line RRF511 contains a 3,564-bp deletion that spans exon 17 and the preceding intronic sequence. The gene-trap plasmid pGT0lxf is integrated immediately after the deletion. Gene-trap vector pGT0lxf contains an intron and splice acceptor (In-SA) followed by the βgeo cDNA, a stop codon, and a polyA addition signal (pA). The positions of oligonucleotide primers within genomic and vector sequences are indicated. (B) Mtmr13 genotyping using primers 599, 600, and 601 in a three-primer PCR. (C) RT-PCR analysis of Mtmr13 mRNAs using brain RNA from wild-type, heterozygous, and Mtmr13−/− mice. Primer pairs were designed to detect either the wild-type (primers 369 and 372) or mutant (primers 369 and 368) Mtmr13 mRNA. ΔEx17 is an mRNA message that results from splicing of exon 16 to exon 18. (D and E) Mtmr13 protein analysis in brain and sciatic nerve, respectively. Immunoprecipitates (IP) and extracts were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting (IB).