Fig. 2.
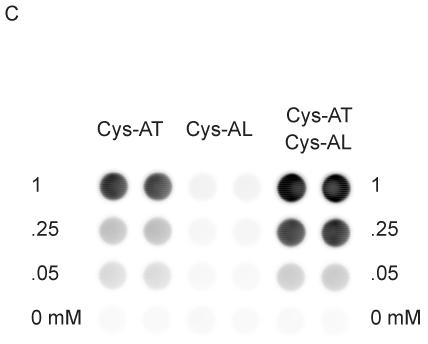
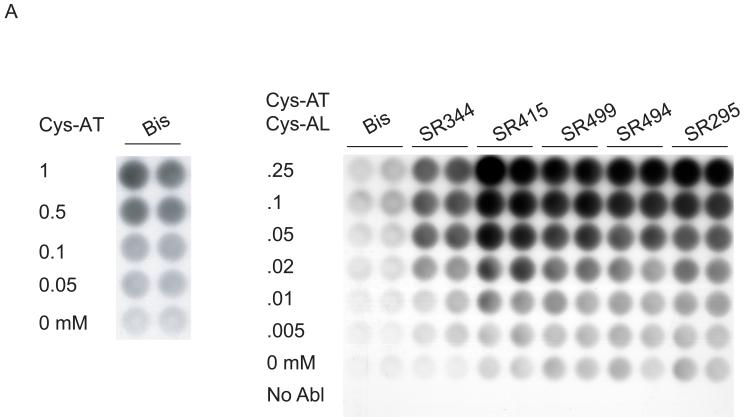
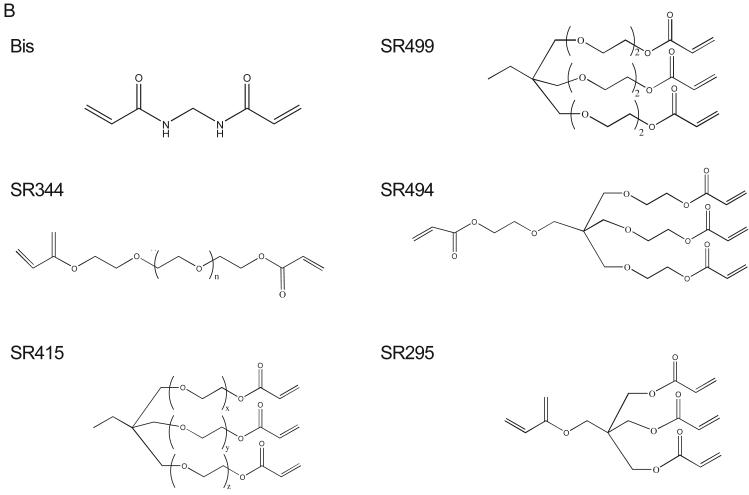
Phosphorylation of peptides by K562 lysates. (A, left) A titration of Cys-Abltide was attached to the surface in duplicate at the indicated concentrations, reacted with 25 μg K562 cell lysate, and detected by antibody and chemiluminiscent reagents as described in Materials and Methods. (A, right) The hydrogel surface was activated and then linked with different bis-, tri-, and tetra-acrylates. Cys-Abltide (Cys-AT) and Cys-Abl ligand (Cys-AL) were added in a 1:1 ratio at 0.25, 0.1, 0.05, 0.02, 0.01 and 0.005 mM. The kinase assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods with detection by chemiluminiscence. (B) Chemical structures of bisacrylamide and the Sartomer bis-, tri-, and tetra-acrylates: SR344, polyethylene glycol (400) diacrylate; SR415, ethoxylated (20) trimethylolpropane triacrylate; SR499, ethoxylated (6) trimethylolpropane triacrylate; SR494, ethoxylated (5) pentaerythritol tetraacrylate; SR295, pentaerythritol tetraacrylate. (C) After activation and SR415 attachment, the wells were treated with the peptides (Cys-AT alone, Cys-AL alone and Cys-AT/Cys-AL combined) in duplicate at the indicated concentrations. The kinase reactions and immunodetection with chemifluorescence were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Image shows accumulation of resorufin, the fluorescent Amplex Red reaction product, proportional to relative phosphorylation in each well.