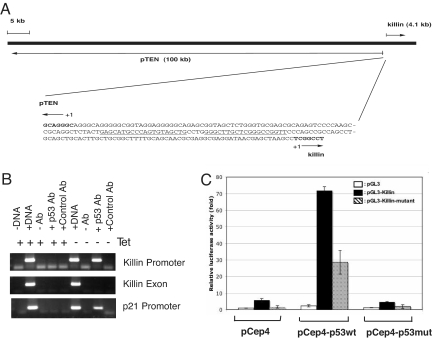
Fig. 2.
Killin is localized in close proximity to the pTEN tumor-suppressor gene and is transcriptionally activated by p53. (A) Chromosomal locus of killin. The 194-bp intergenic region separating killin and pTEN contains a divergent promoter with a p53 consensus-binding site (underlined). Note killin is encoded by a single exon of 4.1 kb, whereas pTEN is encoded by multiple exons and introns spanning >100 kb. (B) ChIP assay showing that p53 binds to the 140-bp killin promoter. The p21 promoter and killin exon were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. (C) luciferase reporter assays showing that the 140-bp killin promoter sequence containing the conserved p53-binding site (pGL3-Killin) conferred a dramatic p53-dependent transcription activation, whereas mutations at the key p53 consensus bases within the Killin promoter (pGL3-Killin-mutant) greatly decreased the p53 effect. Cotransfected vectors expressing either wild-type (pCep4-p53wt) or a DNA-binding mutant of p53 (R248W) (pCep4-p53mut), and the vector control (pCep4), were as indicated.