Fig. 4.
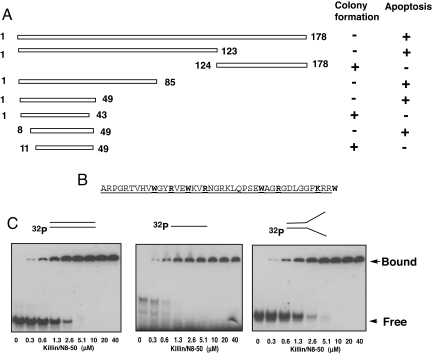
Killin is a high-affinity DNA-binding protein. (A) Bacterial genetic screen and serial deletion analysis of the functional domain of Killin. pQE32 bacterial expression vectors encoding either the full-length N-terminal His-tagged Killin (1–178 aa) or truncated Killin, as indicated, were transformed into either XL-1 blue (lac Iq with repression) or GH1 (wild-type lac I without repression) competent cells and selected with ampicillin in the absence of IPTG. Killin deletions that retained the ability to kill E. coli were scored for their ability to inhibit colony formation in GH1 cells. The same Killin deletion mutants fused to GFP were also transfected into H1299 cells and tested for their ability to cause apoptosis (nuclear condensation) within 36 h. (B) Amino acid sequence of Killin/N8–50 peptide with the minimum 8- to 49-aa residues underlined. (C) In vitro DNA-binding kinetics of Killin/N8–50 peptide. 32-P end-labeled double-stranded, single-stranded, and artificial replication fork DNA templates of 32–35 bases or base pairs in length were each incubated with increasing concentration of Killin/N8–50 peptide, as indicated. The reactions were resolved on a 6% TBE PAGE gel.