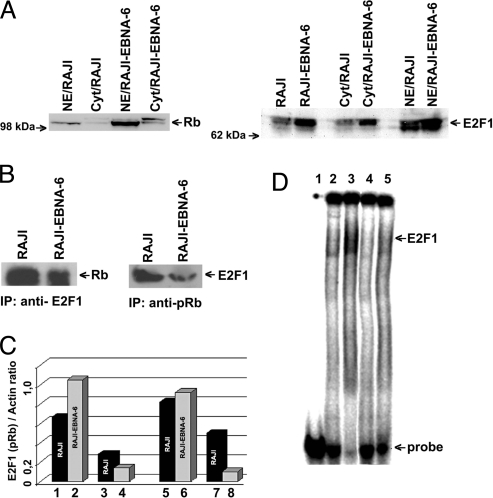
Fig. 7.
S18-2 expression decreases pRb levels. (A) Western blot showing protein levels in the nucleus and cytoplasm of the RAJI-EBNA-6 cells compared with RAJI. Notice the increase in pRb and E2F1 levels when EBNA-6 is expressed. (B) Immunoprecipitations from RAJI and RAJI-EBNA-6 cell lysates. (Left) Precipitations with anti-E2F1 antibody. Notice the decrease in the amount of pRb, bound to E2F1. (Right) Precipitations with anti-pRb antibody. The amount of pRb in complex with E2F1 protein is lower in RAJI-EBNA-6 cells. (C) Levels of total E2F1 and pRb proteins and in complex with each other. Lanes 1 and 2: amount of E2F1 in the RAJI and RAJI-EBNA-6 cell lysate (as a ratio to actin); lanes 3 and 4: amount of E2F1, precipitated with anti-pRb antibody from cell lysates; lanes 5 and 6: amount of total pRb in the cell lysates; lanes 7 and 8: 10-fold magnified amount of pRb, precipitated with anti-E2F1. (D) EMSA of DNA oligo, containing the two binding sites for E2F1. Lane 1: labeled DNA probe; lane 2: DNA probe with RAJI nuclear extract; lane 3: DNA probe with RAJI-EBNA-6 nuclear extract; lane 4: as lane 2 and anti-E2F1 mouse monoclonal antibody; lane 5: as lane 3 and anti-E2F1 antibody. Notice that almost all DNA is bound to E2F1 in RAJI-EBNA-6 cells compared with RAJI cells (lane 3 compared with lane 2). Observe that treatment with anti-E2F1 antibody leads to disappearance of DNA shift (lanes 4 and 5).