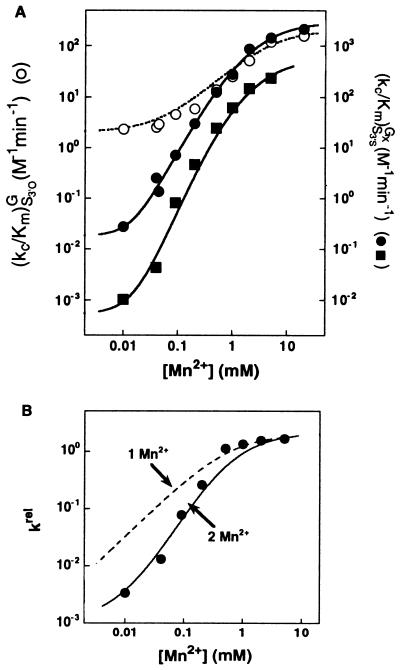
Figure 5.
Two Mn2+ ions are required to rescue the reaction of S3′S with GNH2. (A) Effect of Mn2+ on the reaction E⋅S + GX → products [(kc/Km)GX; GX = G or GNH2] with S3′O and G (○), S3′S and G (●), and S3′S and GNH2 (■). Determined as in Fig. 4 with subsaturating GX. The data for reactions of S3′O with G and of S3′S with G are from Fig. 4A and are shown for comparison. (B) The effect of Mn2+ on the rate of reaction of S3′S with GNH2 relative to that of S3′O with G [krel = (kc/Km)S3′SGNH2/(kc/Km)S3′OG]. The solid line is the Mn2+ concentration dependence of the relative reactivity predicted from a model in which two Mn2+ ions, MnA2+ and MnC2+, independently rescue the reaction of S3′S and GNH2, respectively (see Eq. 2). The dashed line is the best fit of data to a model in which a single Mn2+ ion rescues the reaction of S3′S with GNH2.