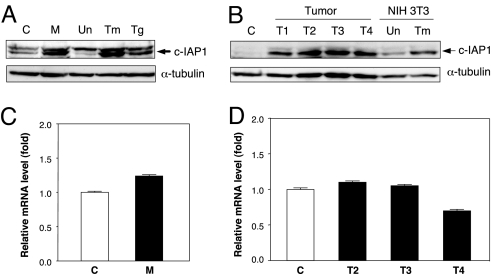
Fig. 5.
Elevation of c-IAP1 in mink cells chronically infected with MCF13 MLV and in virus-induced thymic lymphomas at the posttranscriptional level. (A and B) Detection of c-IAP1 protein by immunoblotting for mink cells either uninfected as control (C) or chronically infected with MCF13 MLV (M) and mink cells either untreated (Un) or treated with tunicamycin (Tm) or thapsigargin (Tg) at 1 μg per ml for 18 h (A) and control thymus (C), thymic tumors (T1-T4), or NIH 3T3 fibroblasts that were either untreated (Un) or treated with tunicamycin (Tm) (B). α-Tubulin was detected as a loading control. (C and D) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of c-IAP1 mRNA in uninfected (C) and chronically infected (M) mink cells shown in A (C) and control thymus and thymic tumors T2-T4 shown in B (D). Mean values calculated from triplicate assays and their ranges are indicated for each cell type. P values that were determined by Student's t test are 0.6 for the comparison between uninfected and chronically infected cells shown in C and 0.09–0.8 for comparisons between the control thymus and thymic tumors shown in D.