Figure 3.
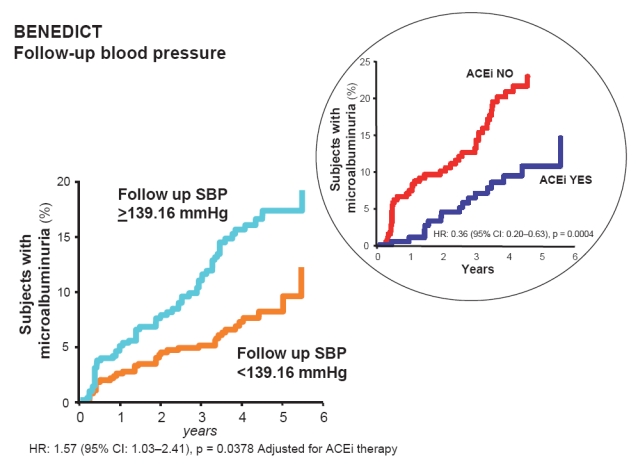
Patients who developed microalbuminuria throughout the study period of the BENEDICT trial according to follow-up systolic blood pressure (SBP). These are patients with type 2 diabetes, arterial hypertension, and normoalbuminuria at baseline. Effective SBP reduction below the median (<139.16 mmHg) has specific and independent protective effects against the development of microalbuminuria. The risk reduction for microalbuminuria that was achieved by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) therapy in patients with follow-up SBP above the median (≥139.16 mmHg) was highly significant even after adjustment for baseline covariates and concomitant treatment with non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. Thus ACEi therapy had a further protective effect, in particular when SBP was less effectively controlled (inset).
