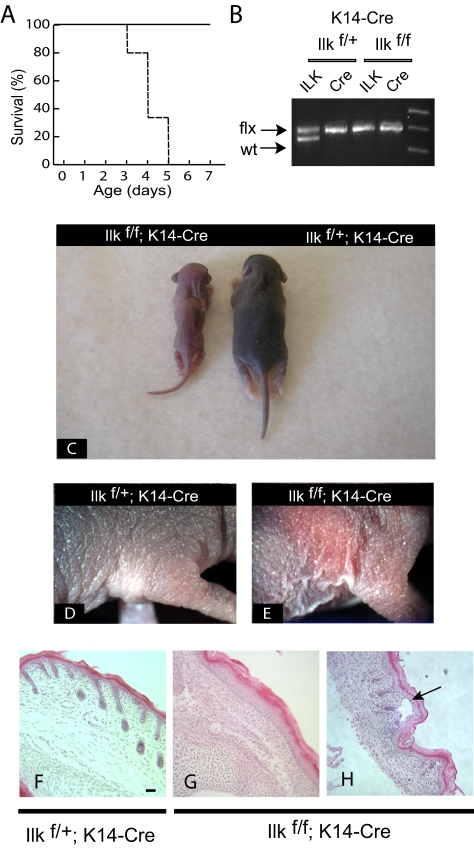
Figure 2.
Phenotypic abnormalities in mice with targeted inactivation of the Ilk gene in the epidermis. (A) Cumulative survival curve (Kaplan-Meier survival plot) of Ilkf/f;K14Cre mice (- - - -) and control Ilkf/+;K14Cre littermates (——, n = 36). (B) Ilkf/f mice were bred with Ilkf/;K14Cre transgenic mice, and their progeny was genotyped for presence the Cre transgene and the mutant, floxed Ilk allele at 4 d of age, using PCR. (C) Visible abnormalities in Ilkf/f;K14Cre mice. The photograph shows the appearance of the animals genotyped in B at 4 d of age. The mouse with ILK-deficient epidermis shows growth retardation and its skin lacks pigmentation, apparent in the ILK-expressing littermate. (D and E) Presence of dry, scaly and fragile skin in the absence of epidermal ILK expression. (F–H) Histological examination of ILK-deficient epidermis reveals abnormally low hair follicle abundance (G) and presence of blisters, where the epidermis has detached from the dermis (arrow in H). Bar, 100 μm.