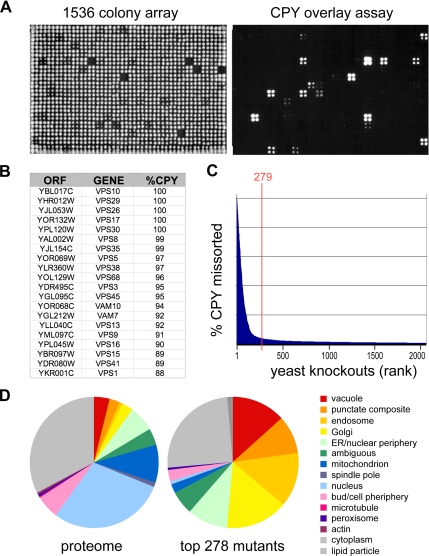
Figure 1.
Genome-scale identification of protein-sorting mutants. (A) Yeast knockout strains were plated as 1536 arrays on solid agar (left) or on agar covered with a nitrocellulose filter. Secreted CPY retained on the filter was visualized by Western blotting (right). (B) Top 20 CPY-secreting mutants. Genome-wide screens for CPY missorting were carried out in duplicate on three independent deletion collections, and a median endosomal-sorting index was computed based on densitometry of digital images. (C) Ranked secretion values for the 2000 top CPY-secreting mutants. The top 279 strains were chosen for further analysis. (D) Pie chart showing the subcellular localization of proteins corresponding to the 279 mutants based on a genome-wide GFP fusion study (Huh et al., 2003). Vacuole, endosome, “punctate composite,” Golgi, and ER localizations were enriched in the mutant set compared with the proteome.