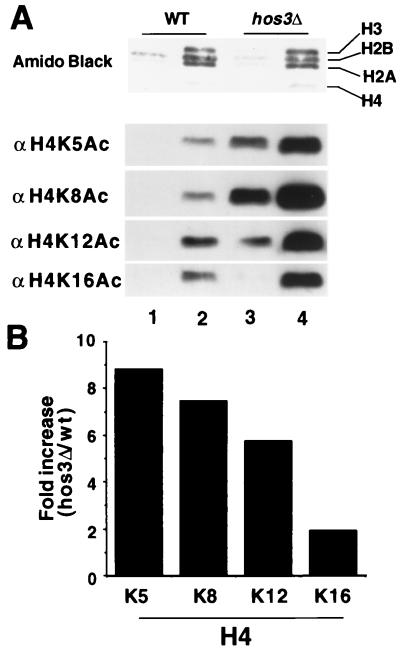
Figure 1.
HOS3 disruption results in histone H4 hyperacetylation. (A) Relative acetylation levels of histone H4 isolated from YDS2 (WT) (lanes 1 and 2) and SRYH3 (hos3Δ) yeast (lanes 3 and 4) were determined by electrophoresing 1 μg (lanes 1 and 3) or 3 μg (lanes 2 and 4) of histones on SDS-polyacrylamide gel. After transfer to PVDF membranes (Millipore) (Experimental Procedures), blots were probed with antibodies specific for H4 acetyl-lysine 5, 8, 12, or 16 (antibodies to be described elsewhere). Protein load was visualized by staining the membrane with amido black. Antibody binding then was detected by using ECL (Amersham) and anti-rabbit Ig HRP-linked antibody (Amersham) as described in Experimental Procedures. (B) Quantitation of increased acetylation levels of histone H4 sites observed for histones isolated from hos3Δ versus wild-type yeast. Western blots in A were reacted with 35S-labeled anti-rabbit Ig, detected by PhosphorImager, and analyzed by using imagequant software as in Experimental Procedures. Quantitation is given as fold increase in acetylation observed for the histones isolated from the SRYH3 strain (hos3Δ) vs. YDS2 (wt).