Figure 3.
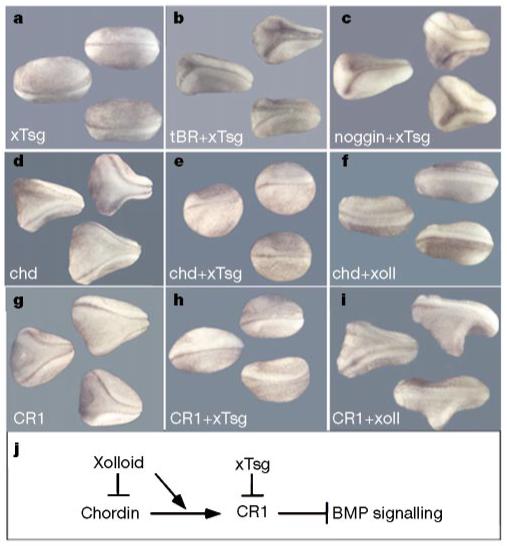
xTsg blocks secondary axis formation by CR1 downstream of Chordin cleavage by Xolloid. a, Microinjection of 250 pg xTsg mRNA. b,c, The induction of secondary axes by 200 pg tBR (dominant-negative BMP receptor; b) or 5 pg noggin mRNA (c) is not affected by co-injection of 250 pg xTsg mRNA. d, Injection of 10 pg chordin mRNA induces the formation of secondary axes that are inhibited by co-injection of 250 pg xTsg mRNA (e) or 200 pg Xolloid mRNA (f). g, Secondary axes induced by injections of 80 pg CR1 mRNA (a 32-fold molar excess compared with full-length chordin mRNA) are inhibited by co-injection of 250 pg xTsg mRNA (h) but not by co-injection of 200 pg Xolloid mRNA (i). Similar results were obtained in at least three independent experiments, with n = 22-52 embryos per mRNA combination. All embryos were injected once ventrally at the eight-cell stage. j, Summary of the epistatic studies. Xolloid inhibits Chordin activity but not that of CR1, and xTsg can block CR1 function. These epistatic analyses place the xTsg ventralizing activity downstream of Xolloid cleavage and upstream of the receptor.
