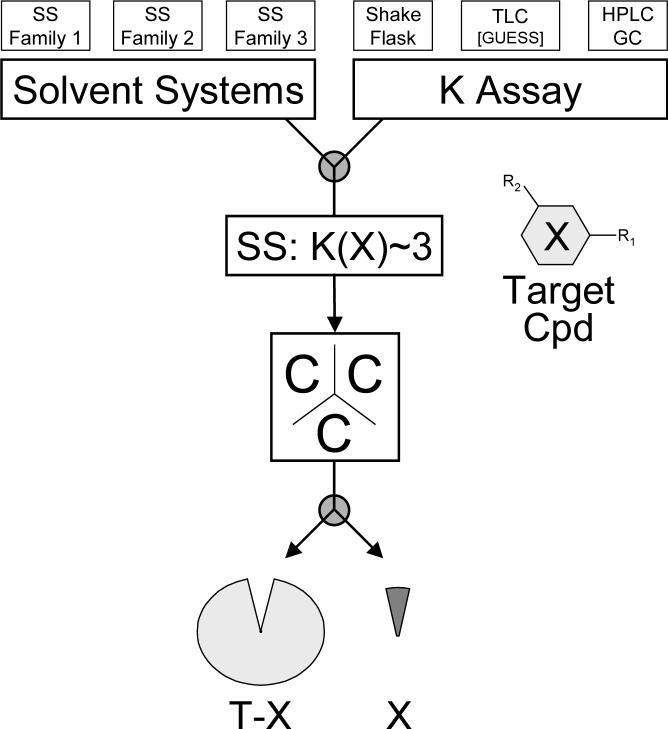
Fig. 3.
General workflow for the chemical subtraction of a target compound (X) from a total plant extract (T) or any other complex (natural) material: A suitable two-phase solvent system (SS) is selected from established or newly designed solvent system families. Utilizing an assay capable of measuring partition coefficients (K), the polarity of a selected SS family is then adjusted to match a suggested target values of K(X) ∼ 3. Subsequent HSCCC fractionation yields the target compound (X) at elution volumes that can be predicted using established CCC theory for elution [19, 37, 38] and extrusion [25, 39]. The surrounding fractions can be recombined to the chemically subtracted starting material, T-X (see discussion for further explanation and references).