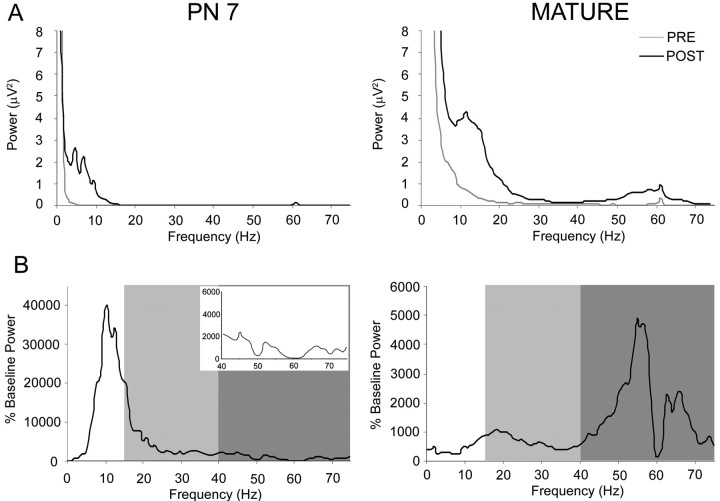
Figure 2.
Comparison of olfactory bulb LFP activity in infant and mature rats presented with isoamyl acetate (150 ppm dilution). A, Mean power spectra of odor-evoked LFP oscillations in the olfactory bulb of 7-d-old and mature rats. Mean power spectra before (pre: thin line) and during (thick line) a 2 s odor stimulus (post). Note the increase in odor-evoked β and γ band oscillations in mature rats compared with 7-d-old rats. B, Mean relative power spectra of odor-evoked LFP oscillations in the olfactory bulb of 7-d-old and mature rats. Mean change in power spectra during a 2 s odor stimulus relative to preodor was expressed for each frequency band relative to the mean baseline power for each frequency within each animal to emphasize difference in odor-evoked power spectra between ages. Mean odor-evoked oscillations increase in the β (light gray) and γ (dark gray) bands in the mature rats as opposed to the theta/low β activity seen in pups. Inset depicts an enlargement of γ power for P7 rats plot on the same power scale as the mature data.